For the first part of this topic see: BIG ESP32 / SX127x topic part 1
For updates to below start topic see: Big ESP32 + SX127x topic part 3
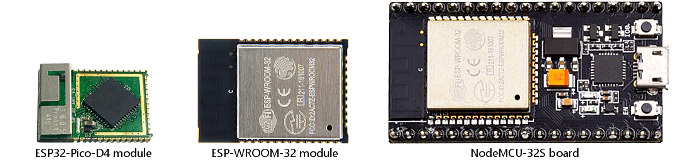
The ESP32 microcontroller and SX127x / RFM9x LoRa transceivers
The ESP32 has built-in support for Wifi and Bluetooth communication but not for LoRa. A SX127x or RFM9x LoRa transceiver adds support for LoRa and the LoRaWAN protocol that are needed for The Things Network.
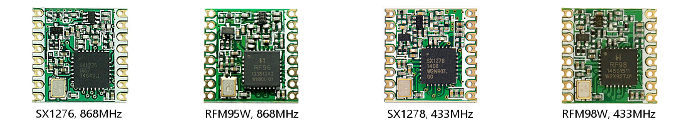
Semtech SX127x LoRa transceivers and HopeRF RFM9x LoRa transceivers are identical. They come in different variants, depending on the targeted frequency band (433, 868 and 915 MHz). Which frequencies are used depends on the geographic region and local ISM band regulations. (HopeRF module numbers usually end with W which stands for ‘international version’.)
The ESP32 and the LoRa transceivers come in several forms:
- On modules.
Modules contain additional components required for making the chips work. The modules use 1.27mm or 2mm pin spacing. For use with breadboards and prototyping PCB with 2.54mm spacing adapters are required. Examples: ESP-WROOM-32 ESP32 module, SX1276 and RFM95 LoRa modules. - On development boards.
Development boards (often) convert to 2.54mm spacing and add additional functionality like power converter, buttons and LEDs. Development boards use either standard modules or separate components. Examples: ESP32 Dev board, Lolin32 and NodeMCU-32S. A pure adapter is the HopeRF RFM95 adapter. - On custom boards which combine ESP32 with a LoRa transceiver.
Custom boards can use standard modules, separate components or a combination of both.
Examples: Heltec Wifi LoRa 32 and TTGO LoRa32.
Software
In addition to the hardware, software is needed for implementing the LoRaWAN protocol. The SX127x LoRa tranceiver provides LoRa radio modulation but it does not implement the LoRaWAN protocol. The protocol has to be implemented in software that needs to run on the ESP32.
The following library implements a LoRaWAN protocol stack that can be used with ESP32: LMIC-Arduino.
The LMIC-Arduino library can be found here: https://github.com/matthijskooijman/arduino-lmic
The library contains examples for implementing a Things Network node for both ABP and OTAA activation.
Try to get the ttn-abp.ino example working first. If that works continue with the ttn-otaa.ino example. When both these examples work then the LoRaWAN part of your setup works. From there you can start adding additional features (e.g. temperature sensor) but get the basics working first.
ABP and OTAA require different settings. See TTN Console and remarks in the sketches for more information.
A nice library for (on-board) (OLED) monochrome displays is: U8g2
The U8g2 library can be found here: https://github.com/olikraus/u8g2
(U8g2 includes U8x8 which is lower on resources.)
ESP32 + SX127x/RFM9x can also be used for implementing a Single Channel Gateway. Information about the Single Channel Gateway software can be found in the following topic: Single Channel Gateway part 3
(See ‘List of single channel gateway implementations / For ESP32’.)
The ESP32 Arduino core (arduino-esp32) now supports the Arduino Boards Manager and is the preferred way to install support for the ESP32 in the Arduino IDE.
See Installing ESP32 support for Arduino IDE using the Arduino Boards Manager.
If you previously manually installed arduino-esp32 from the GitHub repository then don’t forget to remove it.
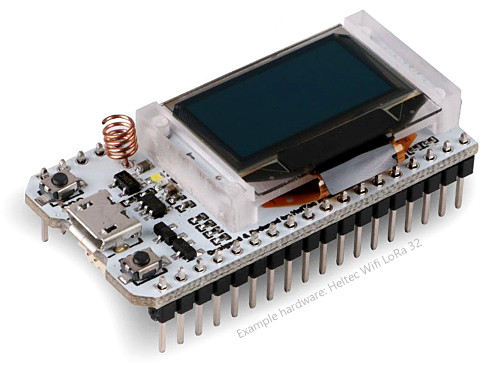
Popular ESP32 LoRa boards
The following boards are popular for prototyping because they combine an ESP32, a LoRa tranceiver, an OLED 128x64 display and LiPo/Li-Ion battery support with charging in one small package that can be used on a breadboard:
- Heltec Wifi LoRa 32
- TTGO LoRa32
These boards come in different versions and there are separate versions for 433/470MHz and 868/915MHz.
LoRa antenna: external, connected via cable with I-PEX connector; 868MHz have 5cm external whip antenna with SMA connector; 433MHz have a helical wire antenna.
WiFi/Bluetooth antenna: single on-board antenna (performance is sub-optimal).
Battery connector: 2-pin Molex PicoBlade (1.25mm spacing). Compatible connectors: ‘JST 1.25mm’ sold on AliExpress and eBay (sold as JST-PH 1.25mm but it is not PH because PH uses 2.0mm spacing).
Be careful with cables that were not included with the board: check first if the colors match the polarity of the board, reversing battery polarity may destroy the board.
There is a dedicated LED (non-programmable) for the battery. It is on when the battery is charged. When no battery is connected: it is off when powered via 3.3V pin but flashes when powered via USB or 5V pin.
A second LED (white on Heltec, blue on TTGO) (programmable) is connected to pin 25, on TTGO V2 the LED is connected to pin 22 but it is useless (see below).
There have been issues with some pigtail cables and some TTGO boards where components were not properly soldered. For more information about these issues check part 1 of this topic.
Note: Sometimes new revisions of boards are released. It is often not be possible to determine the specific revision from the outside of the board. It is possible that a new revision may use different GPIO port(s) for an existing feature. In which case, at first, the board may look defective.
In that case check this article for possible updates and please share your findings when you detect any new changes.
LoRa Performance
The LoRa performance of the Heltec and TTGO boards has shown to be sub-optimal. Important factors are the quality of the RF circuitry (design) and the antennas. The TTGO LoRa32 V2 uses a separate (and shielded) LoRa module which is better than the other models. For a review where the LoRa performance is measured with a spectral analyzer see this ESP32 + LoRa video from Andreas Spiess.
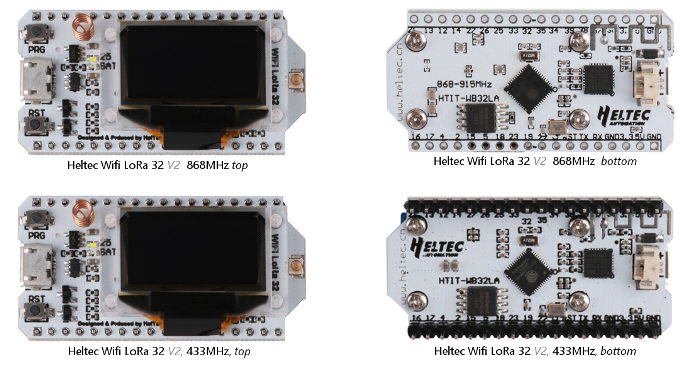
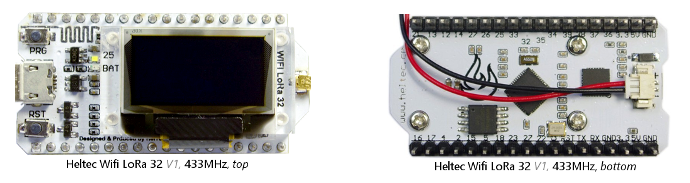
Heltec Wifi LoRa 32
Have a white PCB and come in two different versions (the version numbers are not used by Heltec):
- V1: with on-board PCB WiFi/Bluetooth antenna. Appears to be available for 433MHz only.
-
V2: with small on-board helical antenna (has a PCB antenna on the bottom but that is not connected).
Heltec Wifi LoRa 32 pinout diagram.
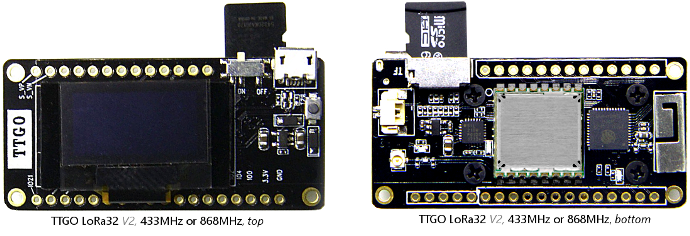
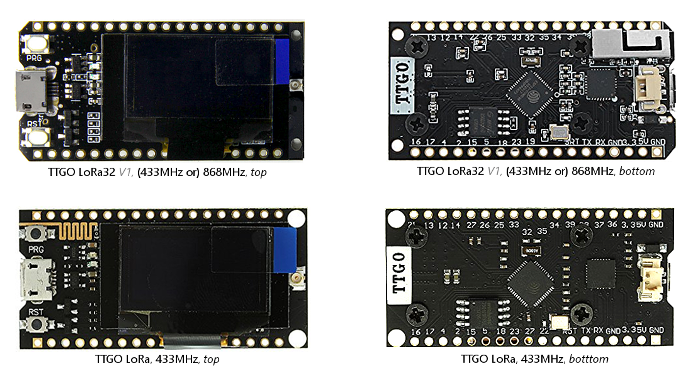
TTGO LoRa and TTGO LoRa32
Have a black PCB and come in several different versions:
-
LoRa with on-board PCB Wifi/Bluetooth antenna on top. Appears to be available for 433MHz only(?). Also available without the display.
-
LoRa32 V1: with on-board metal Wifi/Bluetooth antenna on bottom. I-Pex connector located on top.
-
LoRa32 V2: with on-board metal Wifi/Bluetooth antenna on bottom (in a different location).
Uses ESP32-Pico-D4 (with integrated flash memory) instead of ESP32, uses a (shielded) LoRa module, I-Pex connector located on the bottom, micro-USB connector is rotated 90 degrees, in addition has a microSD card slot on the bottom and an on/off switch for the battery next to the micro-USB connector. Switches the battery only so not possible to switch the board off when connected to USB for charging the battery.
‘Programmable’ LED on pin 22 instead of pin 25 but useless because wired to SCL and all three LEDs are on the bottom side where you cannot see them. DIO1 and DIO2 each have a separate board pin but neither of them is connected to a GPIO port so must be explicitly wired. This also means that the TTGO V2 has two GPIO ports less that could otherwise have been used for other purposes.
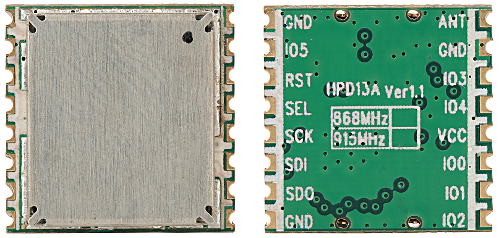
The microSD card slot can be used as a regular SD card reader/writer. The LoRa modules are HPD13A and HPD14A from HPDTek.
New updated pinout diagram v3.0 is available here: TTGO LoRa32 V2.0 Pinout v3.0.pdf (2.3 MB) -
LoRa32 V2.1: Like V2.0 with several changes and improvements (e.g. SMA LoRa antenna connector, different battery charging chip, different switch). Some changes in use of pins / GPIO’s. Different versions of this board exist (some differences in GPIO/pin mappings between versions).
TTGO LoRa32 V2.1 pinout diagram possibly not up to date. Do not use this pinout for LoRa32 V2.1 with PCB marked V1.6 because it is incompatible.
PIN Mappings
Heltec Wifi LoRa 32, TTGO LoRa and TTGO LoRa32 V1:
ESP32 LoRa (SPI) Display (I2C) LED
----------- ---------- ------------- ------------------
GPIO5 SCK SCK
GPIO27 MOSI MOSI
GPIO19 MISO MISO
GPIO18 SS NSS
GPIO14 RST
GPIO26 DIO0
GPIO33 DIO1
GPIO32 DIO2
GPIO15 SCL
GPIO4 SDA
GPIO16 RST
GPIO25 Heltec, TTGO LoRa32
GPIO2 TTGO LoRa
TTGO LoRa32 V2:
ESP32 LoRa (SPI) Display (I2C) LED
----------- ---------- ------------- ------------------
GPIO5 SCK SCK
GPIO27 MOSI MOSI
GPIO19 MISO MISO
GPIO18 SS NSS
EN RST RST
GPIO26 DIO0
GPIO33 DIO1 (see #1)
GPIO32 DIO2 (see #2)
GPIO22 SCL SCL
GPIO21 SDA SDA
GPIO22 useless (see #3)
- Required (used by LMIC for LoRa).
Not on-board wired to any GPIO. Must be manually wired. - Optional (used by LMIC for FSK but not for LoRa).
Not on-board wired to any GPIO. When needed: must be manually wired. - GPIO22 is already used for SCL therefore LED cannot be used without conflicting with I2C and display.
Board definitions
Currently the only board type defined (in ESP32 Arduino Core) is ‘Heltec Wifi LoRa 32’. Select this board type for both Heltec and TTGO boards. Check Pin Mappings above for differences / inconsistencies with a specific board.
Default definitions for board type 'Heltec Wifi LoRa 32':
(Numbers represent GPIO ports)
SCK = 5
MOSI = 27
MISO = 19
SS = 18
SCL = 22
SDA = 21
LED_BUILTIN = 25
How to setup the software
How to configure LMIC with the ESP32 pins used for the LoRa module:
//LMIC LoRa module pin configuration
//For Heltec Wifi LoRa 32, TTGO LoRa and TTGO LoRa32 V1 use:
const lmic_pinmap lmic_pins = {
.nss = 18,
.rxtx = LMIC_UNUSED_PIN,
.rst = 14,
.dio = {/*dio0*/ 26, /*dio1*/ 33, /*dio2*/ 32}
};
//For TTGO LoRa32 V2 use:
//Note: LoRa32 V2 DIO1 and DIO2 are not on-board wired to any GPIO.
//These need to be wired manually.
const lmic_pinmap lmic_pins = {
.nss = 18,
.rxtx = LMIC_UNUSED_PIN,
.rst = LMIC_UNUSED_PIN,
//If DIO2 is not connected use:
.dio = {/*dio0*/ 26, /*dio1*/ 33, /*dio2*/ LMIC_UNUSED_PIN}
//If DIO2 is connected use:
//.dio = {/*dio0*/ 26, /*dio1*/ 33, /*dio2*/ 32}
}
//For TTGO LoRa32 V2.1:
//The first revision(s) does not have LoRa RST connected to GPIO, use as V2 above.
//Revision V1.5 (V1.5 marked on PCB) uses GPIO12 for LoRa RST.
//Revision(s) newer than V1.5 use GPIO19 for LoRa RST.
//Note: On first revision(s) DIO1 and DIO2 are not on-board wired to any GPIO and have to be wired manually.
//Later revisions may have these wired on-board already.
const lmic_pinmap lmic_pins = {
.nss = 18,
.rxtx = LMIC_UNUSED_PIN,
//For board revision V1.5 use GPIO12 for LoRa RST
.rst = 12,
//For board revision(s) newer than V1.5 use GPIO19 for LoRa RST
//.rst = 19,
//If DIO2 is not connected use:
.dio = {/*dio0*/ 26, /*dio1*/ 33, /*dio2*/ LMIC_UNUSED_PIN}
//If DIO2 is connected use:
//.dio = {/*dio0*/ 26, /*dio1*/ 33, /*dio2*/ 32}
}
How to setup U8g2/U8x8 with the ESP32 pins used for the OLED display:
//U8x8 display library configuration
//See U8g2/U8x8 documentation for available display write functions
#include <U8x8lib.h>
//For Heltec Wifi LoRa 32, TTGO LoRa and TTGO LoRa32 V1 use:
U8X8_SSD1306_128X64_NONAME_HW_I2C display(/*rst*/ 16, /*scl*/ 15, /*sda*/ 4);
//For TTGO LoRa32 V2 use:
U8X8_SSD1306_128X64_NONAME_HW_I2C display(/*rst*/ U8X8_PIN_NONE);
//Add to setup():
display.begin();
display.setFont(u8x8_font_victoriamedium8_r); //Optional, more fonts are available.
Example hardware
Below pictures show an overview of available hardware and their appearance. All pictures have the same size ratio for a realistic comparison.
ESP32 modules / boards
LoRa Tranceiver modules
Heltec boards
TTGO boards

 Maybe I have some time for a walk through the neighborhood this evening.
Maybe I have some time for a walk through the neighborhood this evening.